Metallaphotoredox CO2 Extrusion/Recombination
C. C. Le, D. W. C. MacMillan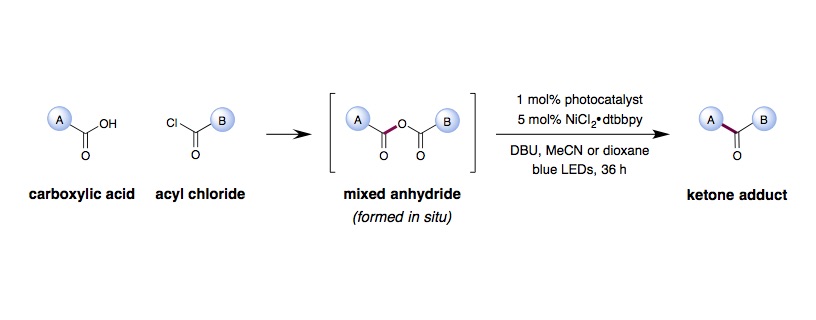
Light source:
Kessil Blue LED lamp. Up to 0.5 mmol scale, one lamp is sufficient. Above 0.5 mmol scale, 2 lamps are recommended.
General procedure:
For N-Boc pyrrolodine-containing carboxylic acids:
To an oven-dried 40 mL vial equipped with a stir bar (cross-shaped) was added Ir[dF(CF3)ppy]2(dtbbpy)PF6 (0.05 mmol, 1 mol%), NiCl2⋅glyme (0.025 mmol, 5 mol%), 4,4¢-dimethoxy-2,2¢-bipyridine (0.025 mmol, 5 mol%), carboxylic acid (0.65 mmol, 1.3 equiv.), and MeCN (25 mL, 0.02 M). The vial was sealed and placed under nitrogen before the acid chloride (0.50 mmol, 1.0 equiv.) was added followed by DBU (0.65 mmol, 1.3 equiv.). DBU must be added after the acyl chloride. The reaction mixture was degassed by sparging with nitrogen while stirring for 30 min before sealing the vial with parafilm. The reaction was stirred and irradiated with a 34 W blue LED lamp (7 cm away, with a cooling fan to keep the reaction temperature at 25 ºC) for 36 hours. The reaction was quenched by exposure to air. The reaction mixture was filtered, then concentrated in vacuo. Purification by column chromatography on silica gel yielded the ketone product.
For all other carboxylic acids:
To an oven-dried 8 mL vial equipped with a stir bar (1/2” x 1/8”) was added Ir[dF(OMe)ppy]2(dtbbpy)PF6 (0.005 mmol, 1 mol%), NiCl2⋅glyme (0.025 mmol, 5 mol%), 4,4¢-dimethoxy-2,2¢-bipyridine (0.025 mmol, 5 mol%), carboxylic acid (0.50 mmol, 1.0 equiv.), and dioxane (5 mL, 0.1 M). The vial was sealed and placed under nitrogen before the acid chloride (0.50 mmol, 1.0 equiv.) was added followed by DBU (0.65 mmol, 1.3 equiv.). DBU must be added after the acyl chloride. The reaction mixture was degassed by sparging with nitrogen while stirring for 30 min before sealing the vial with parafilm. The reaction was stirred and irradiated with a 34 W blue LED lamp (7 cm away, with a cooling fan to keep the reaction temperature at 25 ºC) for 36 hours. The reaction was quenched by exposure to air. Reaction mixture was filtered, then concentrated in vacuo. Purification by column chromatography on silica gel yielded the ketone product.
Tips and tricks:
- The reaction has been run on up to 5.0 mmol scale, with no loss of efficiency. Just use 2 LED lamps for these large scale reactions.
- We observed that the success of the reaction relies heavily on the medium of the reaction. As reported, MeCN and dioxane were the two best solvents. However, other unreported compounds have been shown to work better in toluene and DME.
- In addition, small changes in the ligand system of the nickel catalyst can also result in drastic change in efficiency. Among common bpy-type ligands, the four most successful ligands for this reaction are: 2,2¢-bipyridine, 4,4¢-di-t-butyl-2,2¢-bipyridine, 4,4¢-dimethoxy-2,2¢-bipyridine, and 1,10-phenanthroline.
- The reaction is efficient using a 1:1 ratio of carboxylic acid and acyl chloride. In some cases, increasing the equivalent of carboxylic acid gives a boost in yield. However, increasing the amount of acyl chloride often leads to diminished yield.